Two steps forward, one step backward Backward compatibility in Elasticsearch Alexander Reelsen alex@elastic.co | @spinscale
A presentation at Jcon 2020 in October 2020 in by Alexander Reelsen

Two steps forward, one step backward Backward compatibility in Elasticsearch Alexander Reelsen alex@elastic.co | @spinscale

Today’s goal Think about your own services and how to provide BWC guarantees and help users upgrade!
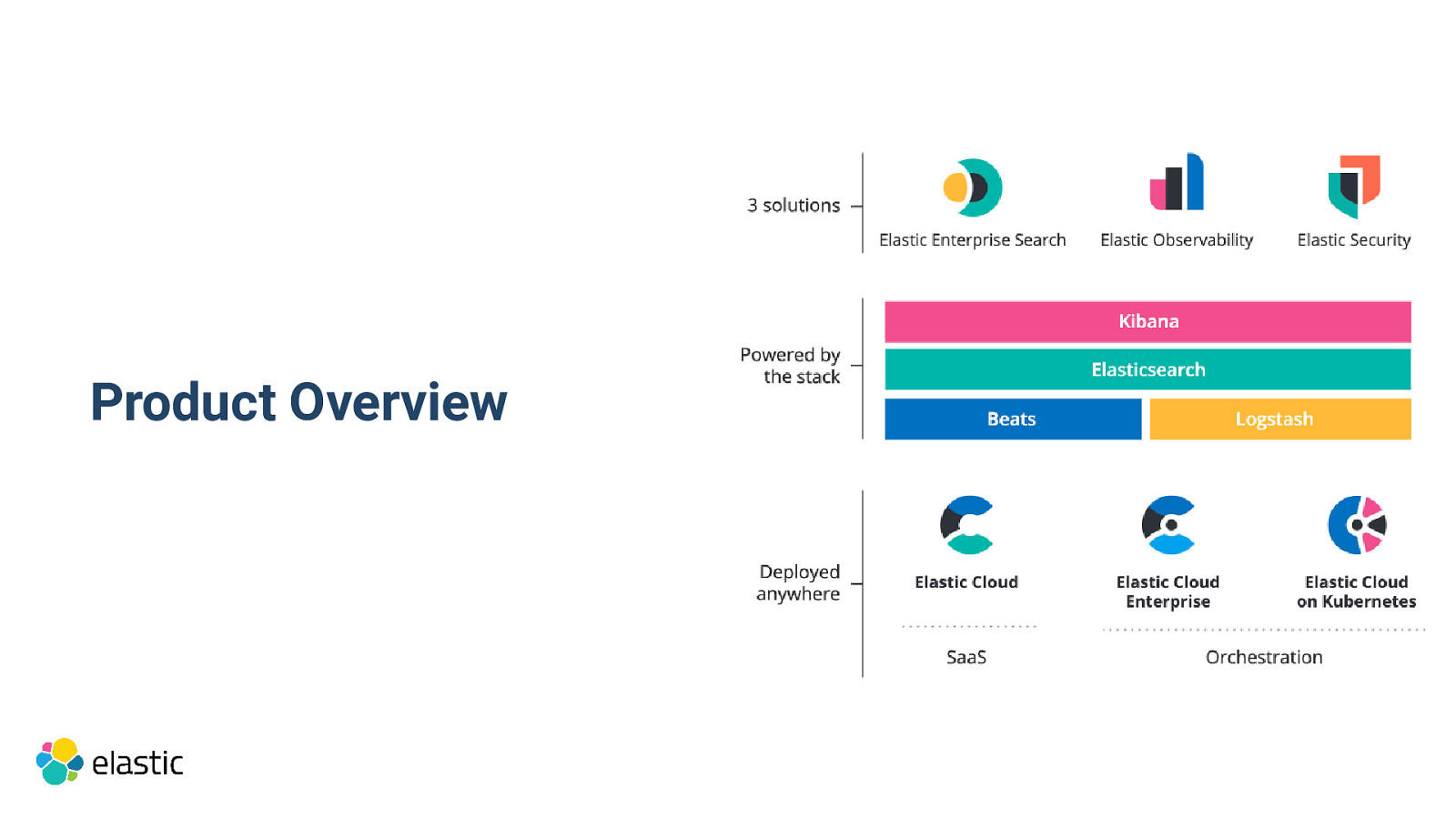
Product Overview

Elastic Stack

Elasticsearch in one minute Search Engine (FTS, Analytics, Geo), near real-time Distributed, scalable, highly available, resilient Interface: HTTP & JSON

What is backward compatiblity?

Why? Running different versions in parallel Upgrades without downtime Reduce version dependencies between client & server

Complexities Lottery: SaaS Ok: API Worst: On-Prem software

Why should users upgrade? Security Bug fixes Functionality Performance Motivation: voluntary or forced ?

What blocks users from upgrading? BWC breaking changes (work before/during upgrade required) Protocol changes (Query DSL changed) Functional changes (Feature removed) Behavioural changes (old data cannot be read)

Semver: Major.Minor.Patch Version Bugfix Major 8.0.0 Minor 7.10.0 Patch 7.9.3
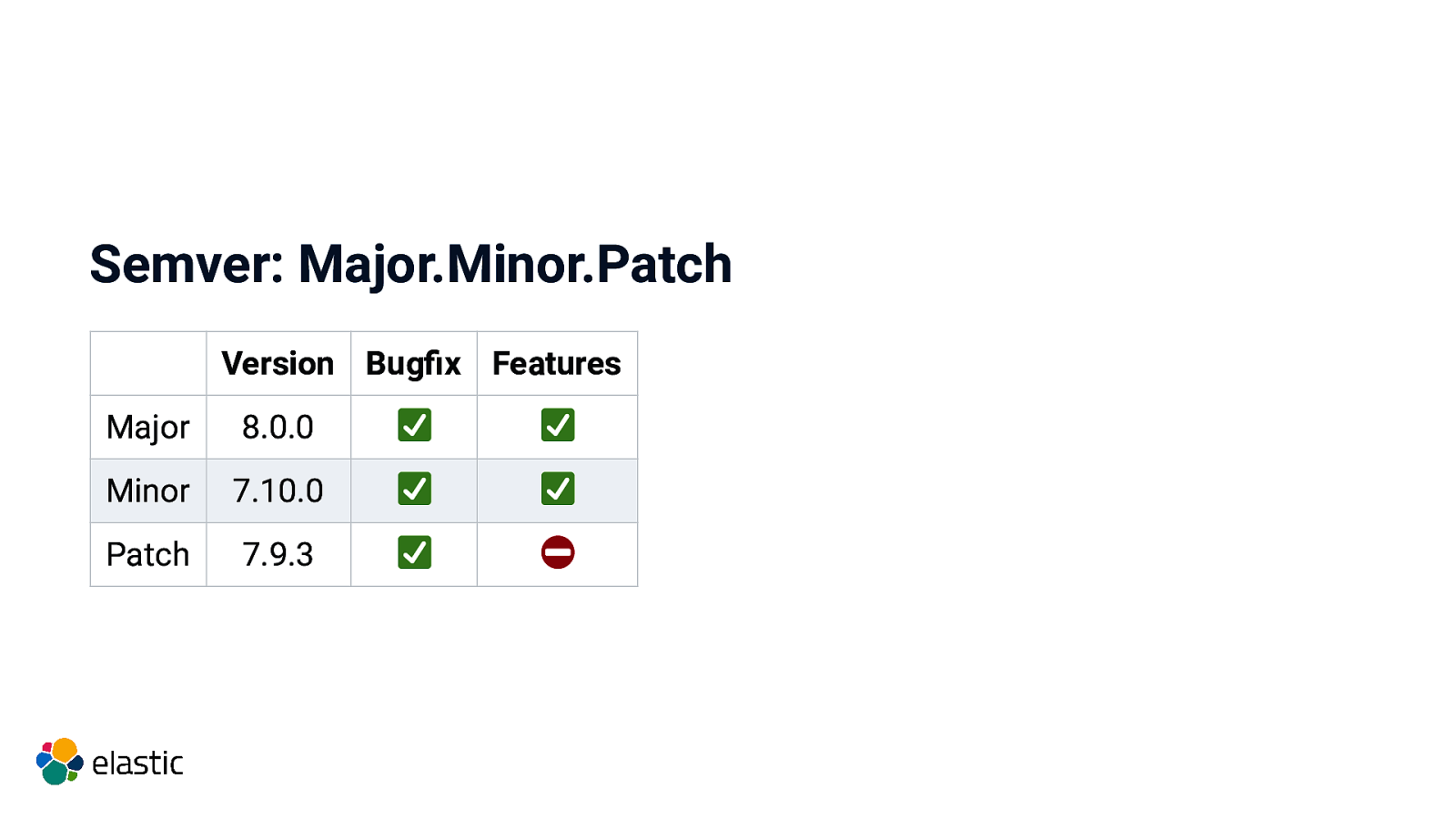
Semver: Major.Minor.Patch Version Bugfix Features Major 8.0.0 Minor 7.10.0 Patch 7.9.3
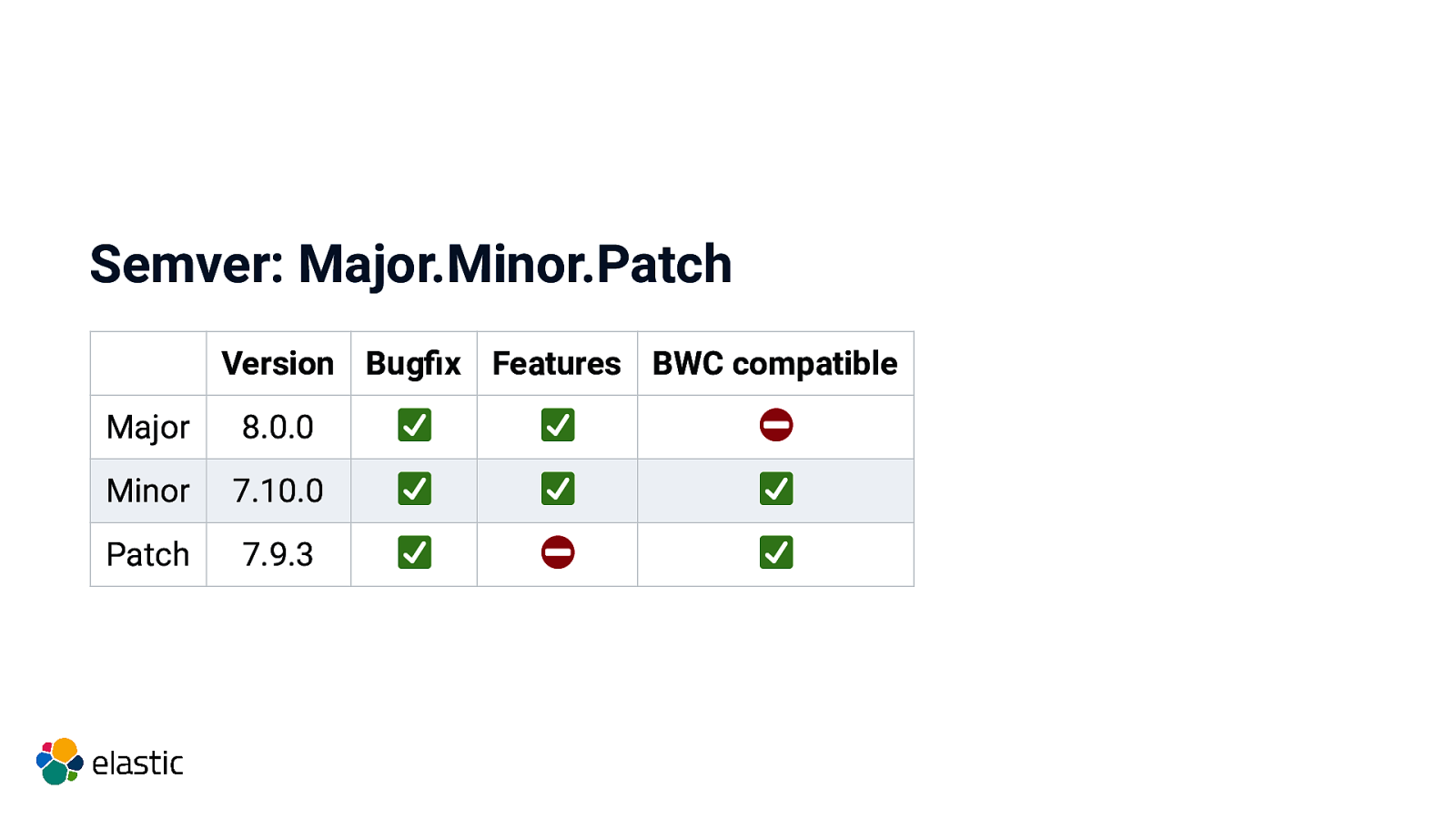
Semver: Major.Minor.Patch Version Bugfix Features BWC compatible Major 8.0.0 Minor 7.10.0 Patch 7.9.3

How to prepare & ease smooth upgrades?

Upgrades Downtime: Full restart No downtime: Rolling node-by-node What about clients communicating with your system?

Compatibility guarantees Data written with a previous major version must be readable Node-to-node communication with a different version must work No need to support all previous versions, just the latest one

Node-to-node communication /** Read from a stream, for internal use only. */ public DateHistogramAggregationBuilder(StreamInput in) throws IOException { super(in); order = InternalOrder.Streams.readHistogramOrder(in); keyed = in.readBoolean(); minDocCount = in.readVLong(); dateHistogramInterval = new DateIntervalWrapper(in); offset = in.readLong(); extendedBounds = in.readOptionalWriteable(LongBounds::new); if (in.getVersion().onOrAfter(Version.V_7_10_0)) { hardBounds = in.readOptionalWriteable(LongBounds::new); } }

How to prepare & present BWC incompatible changes?

Deprecation Logfile/Index/Response header $major-1 can be made ready for upgrade to $major
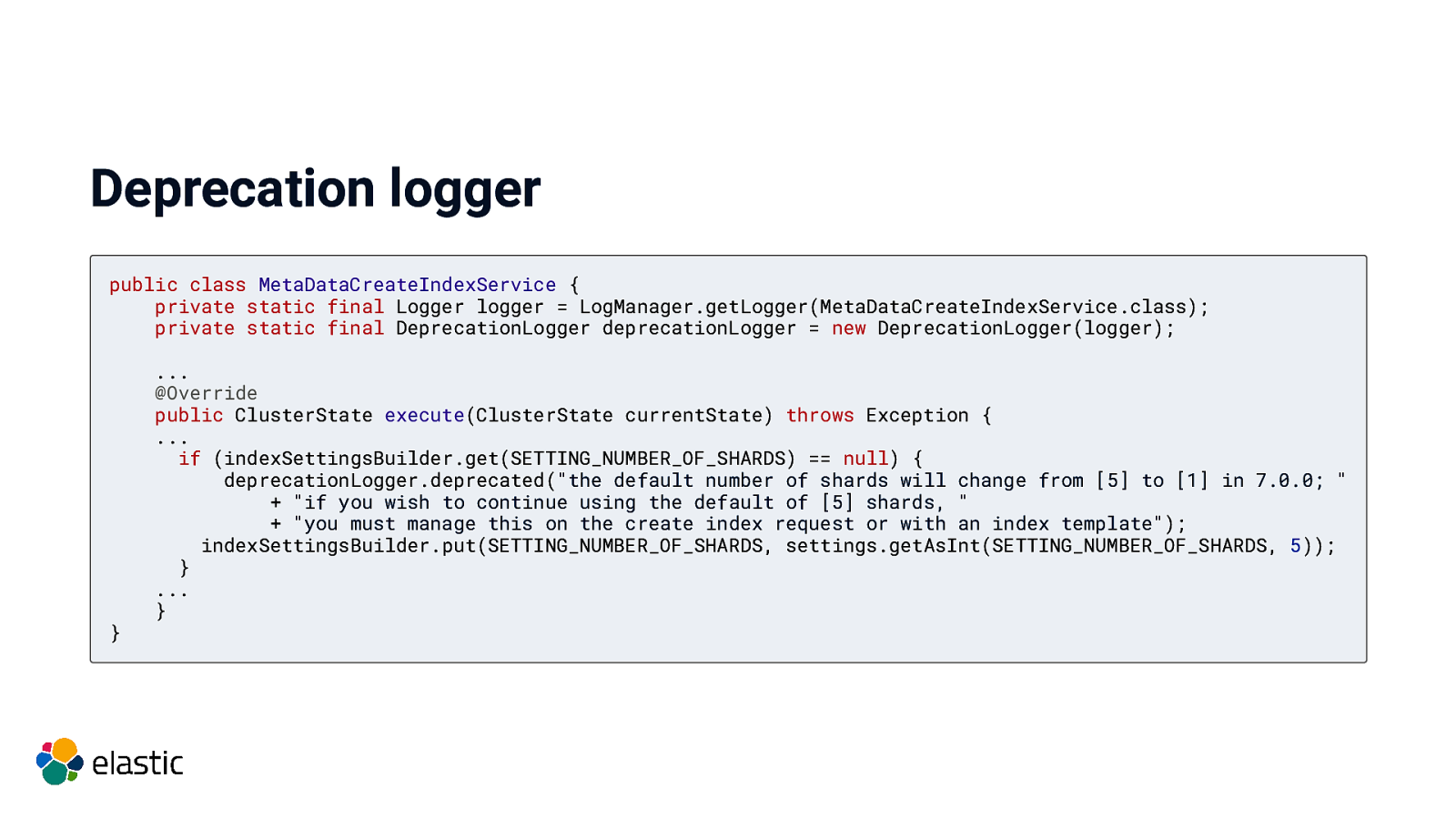
Deprecation logger public class MetaDataCreateIndexService { private static final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(MetaDataCreateIndexService.class); private static final DeprecationLogger deprecationLogger = new DeprecationLogger(logger); } … @Override public ClusterState execute(ClusterState currentState) throws Exception { … if (indexSettingsBuilder.get(SETTING_NUMBER_OF_SHARDS) == null) { deprecationLogger.deprecated(“the default number of shards will change from [5] to [1] in 7.0.0; ” + “if you wish to continue using the default of [5] shards, ” + “you must manage this on the create index request or with an index template”); indexSettingsBuilder.put(SETTING_NUMBER_OF_SHARDS, settings.getAsInt(SETTING_NUMBER_OF_SHARDS, 5)); } … }
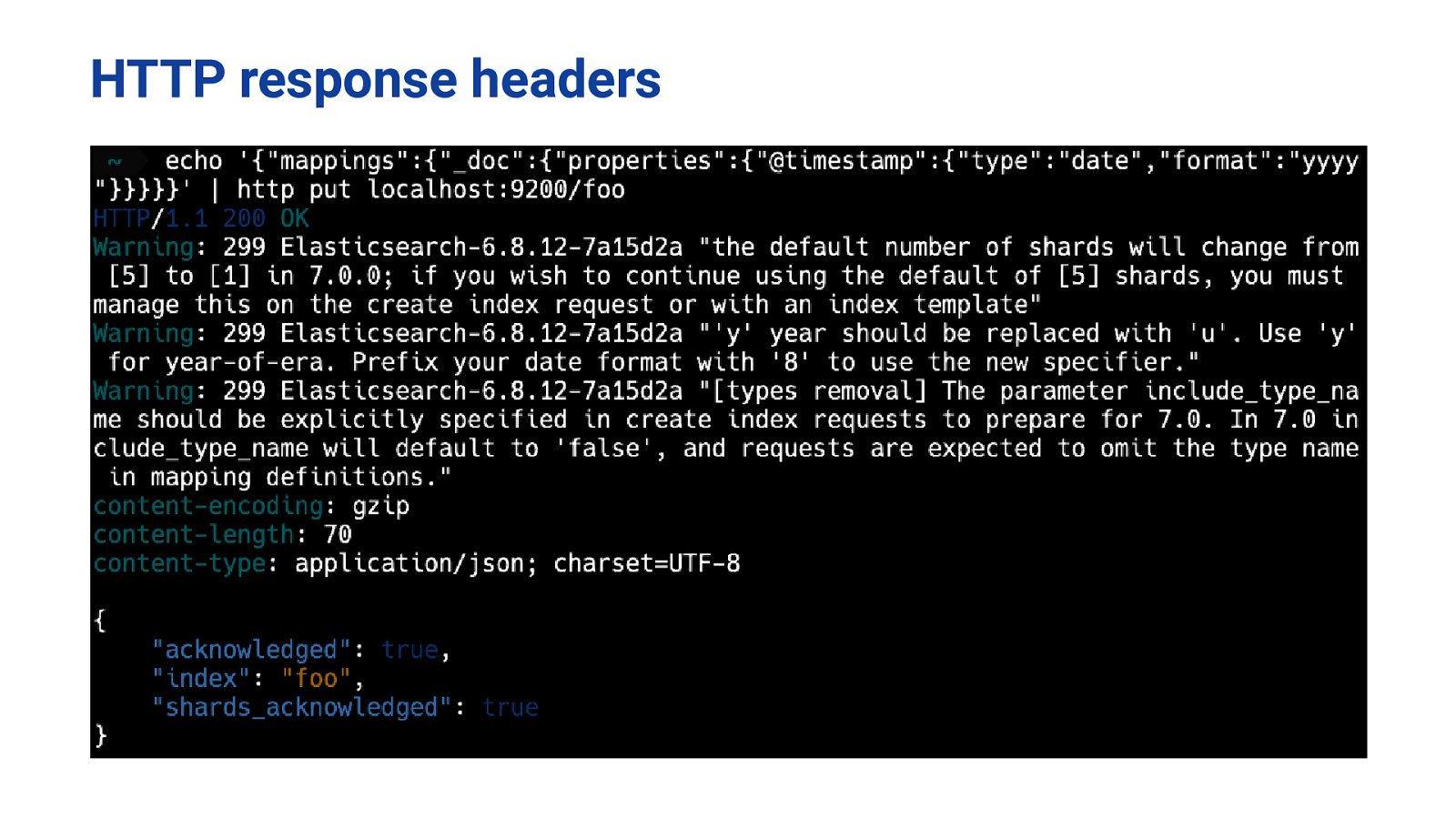
HTTP response headers
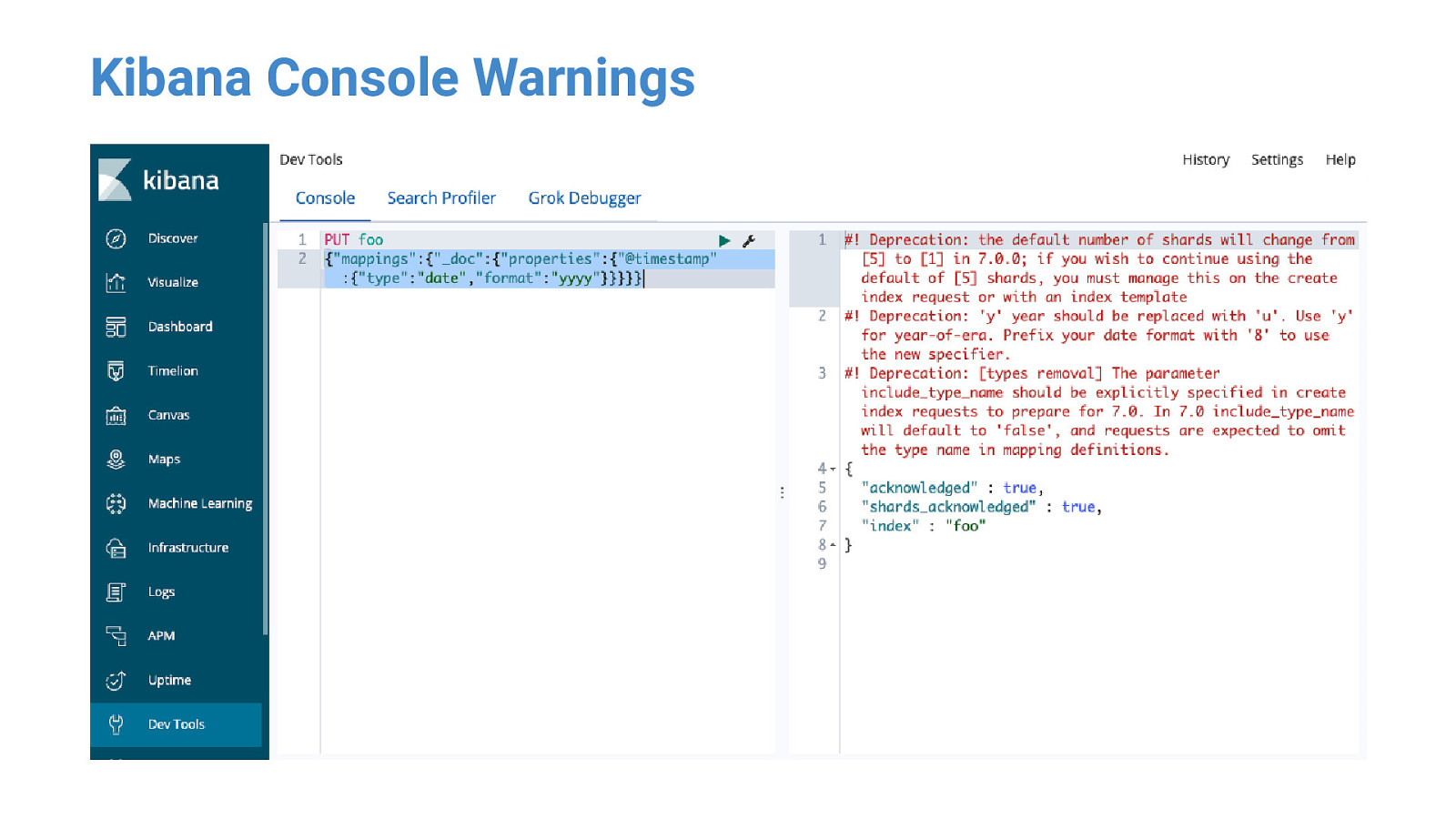
Kibana Console Warnings
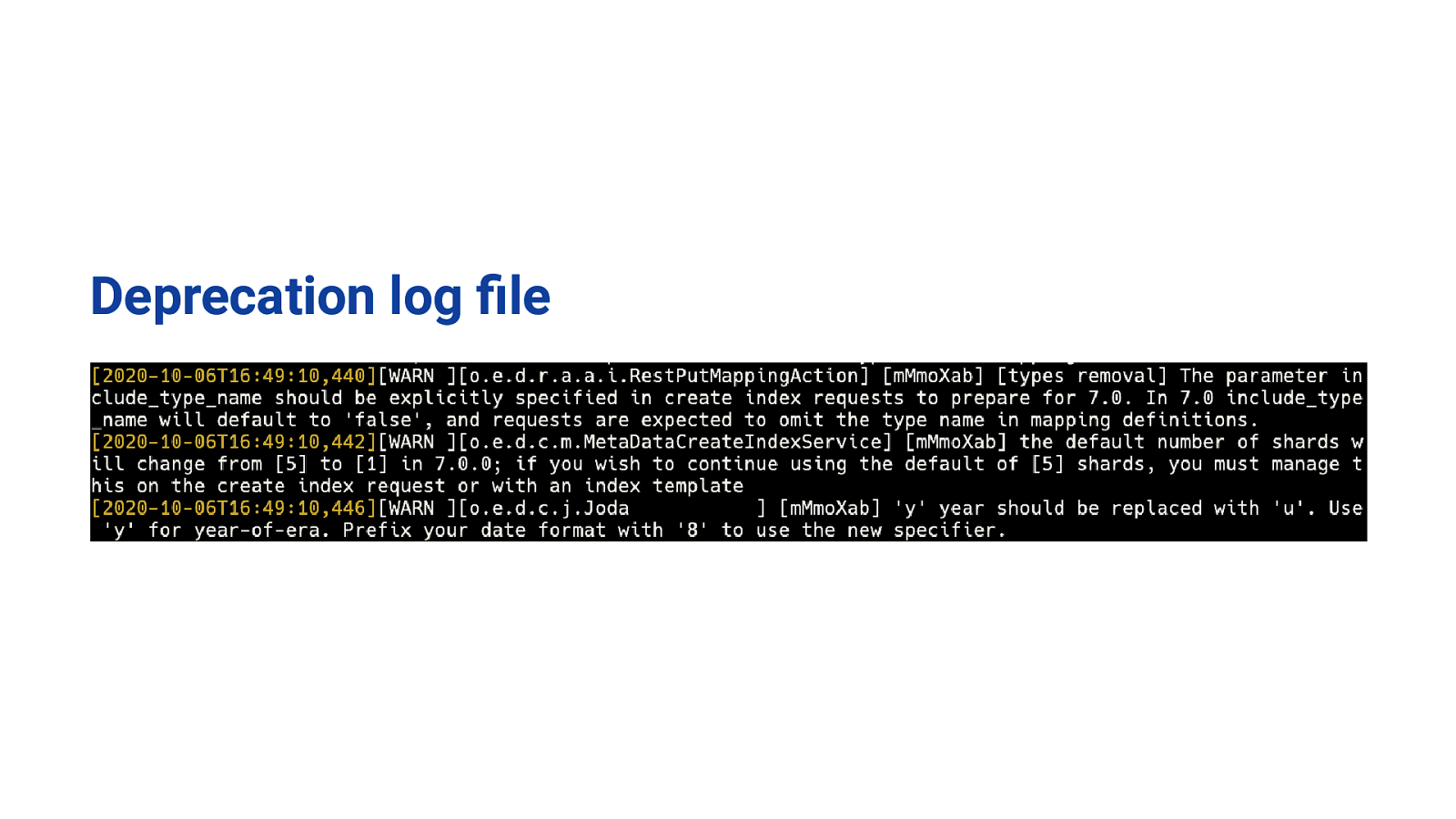
Deprecation log file

No one is reading ANY of these!
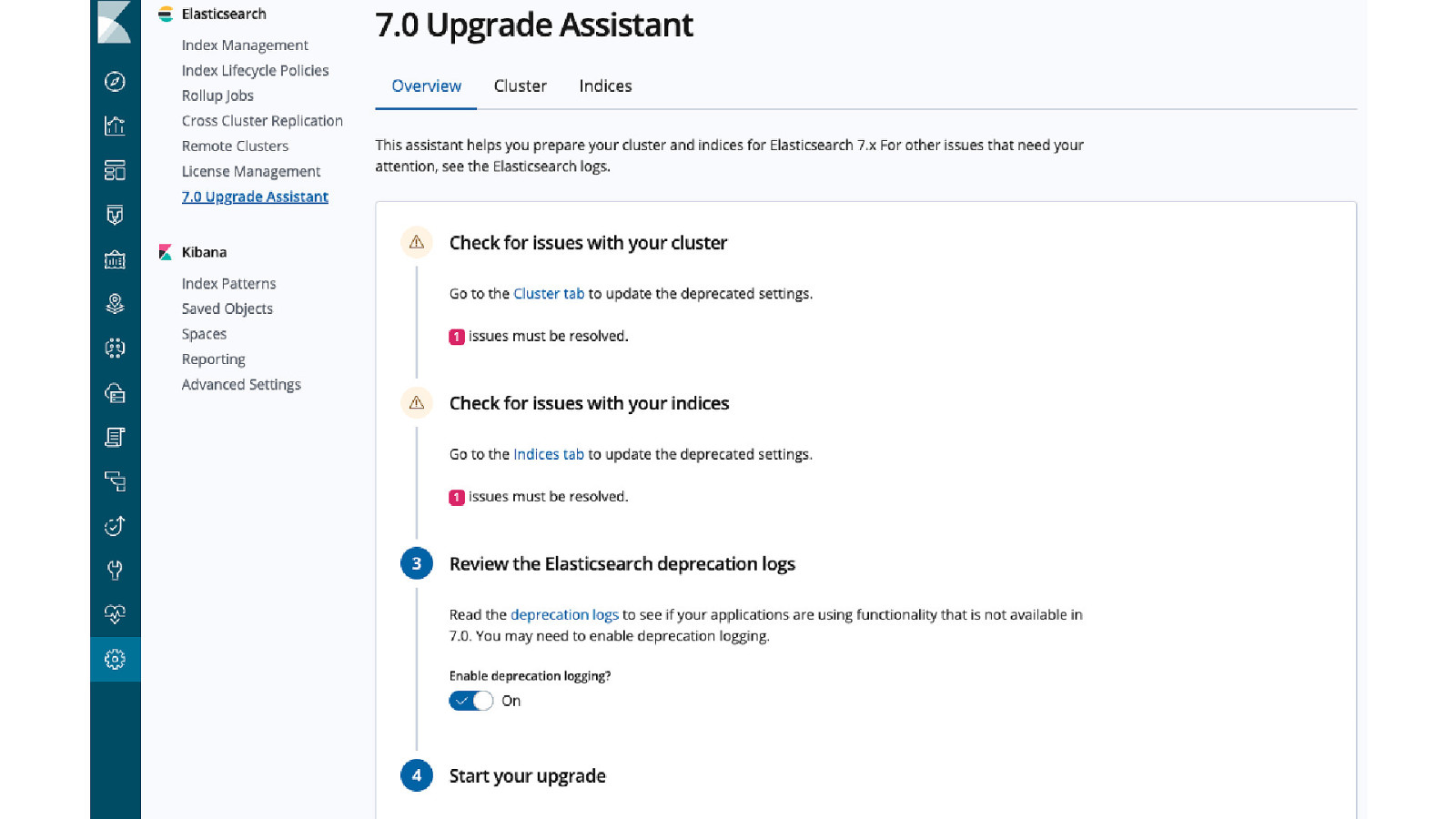
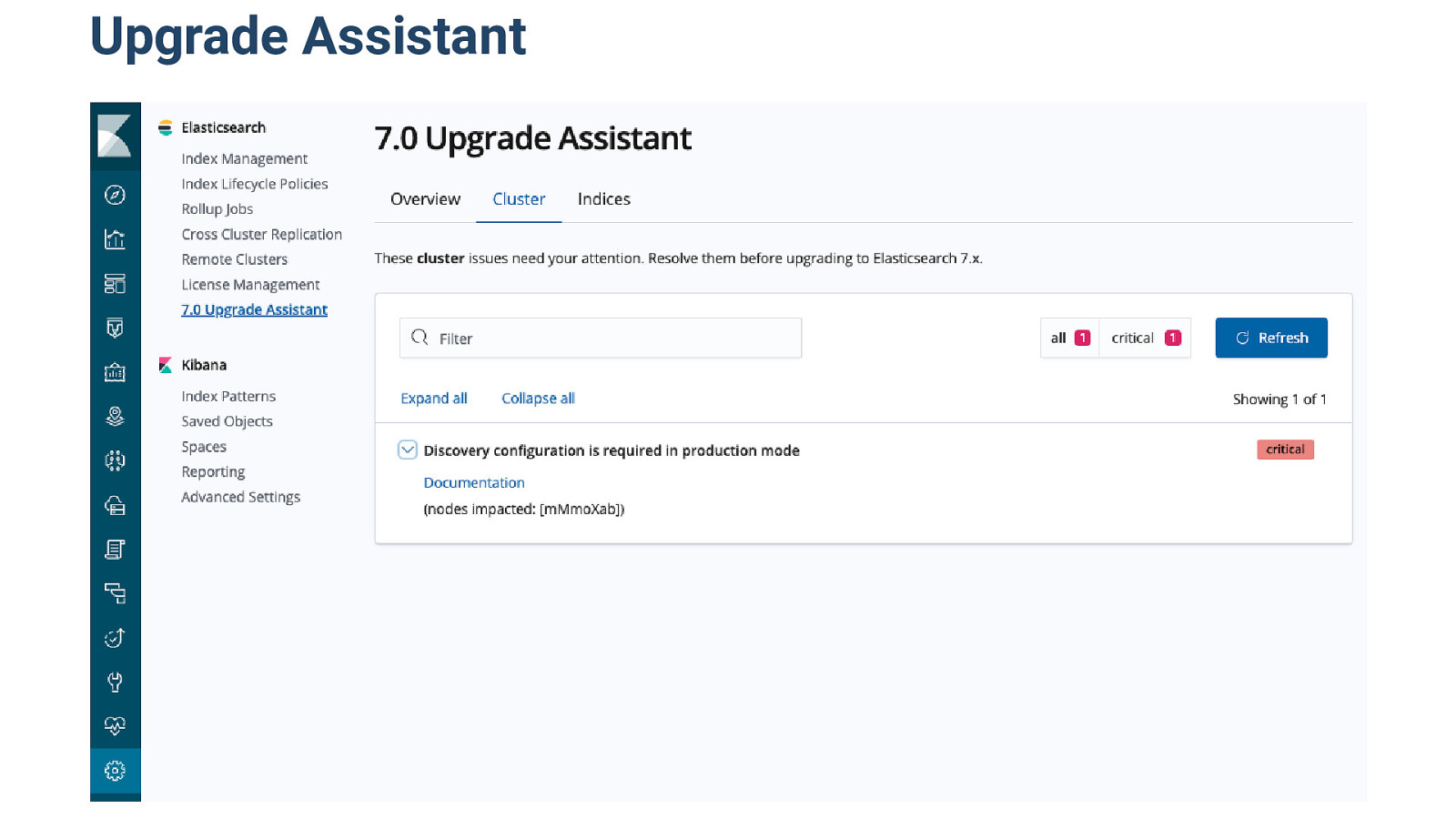
Upgrade Assistant
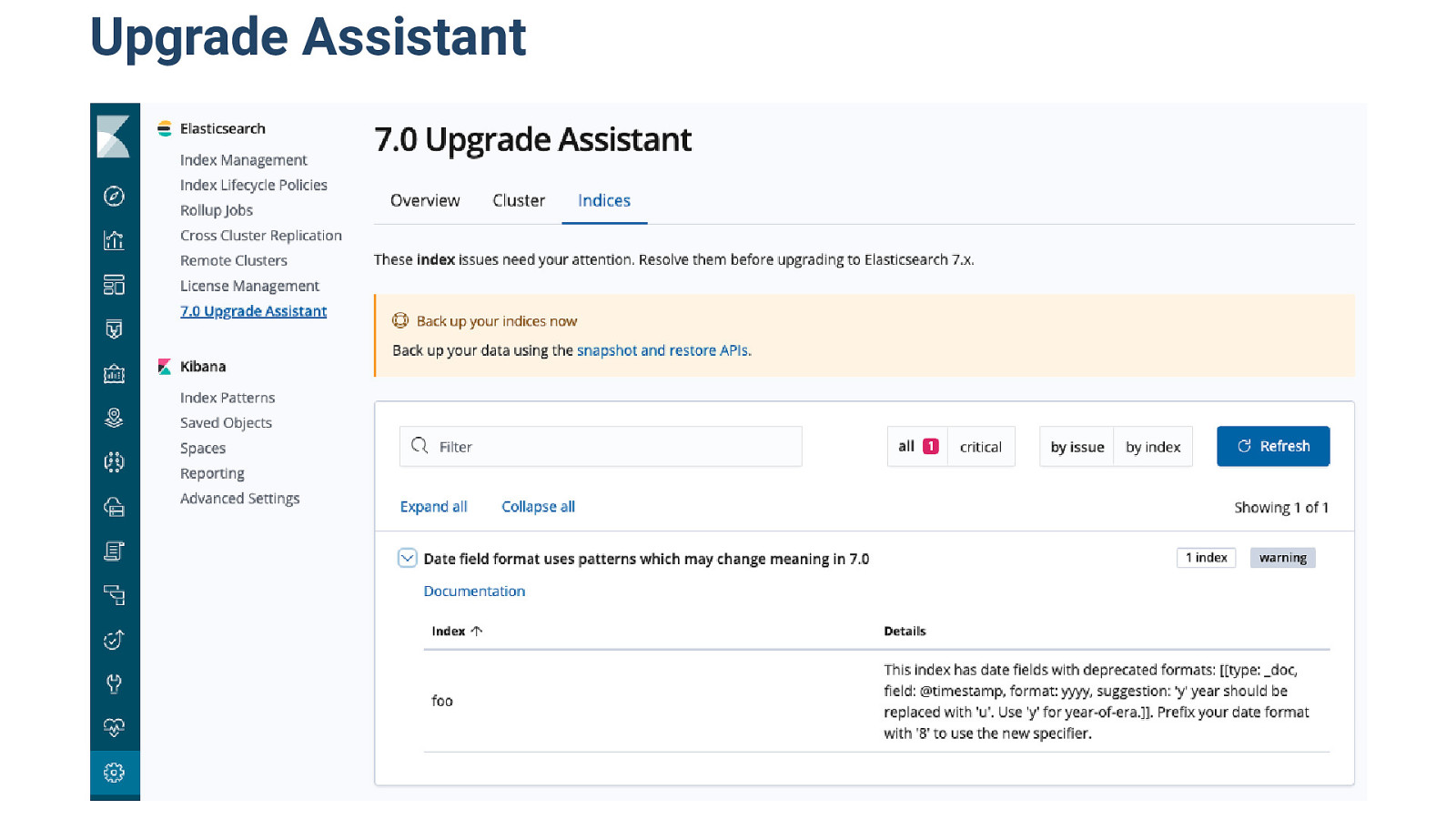
Upgrade Assistant
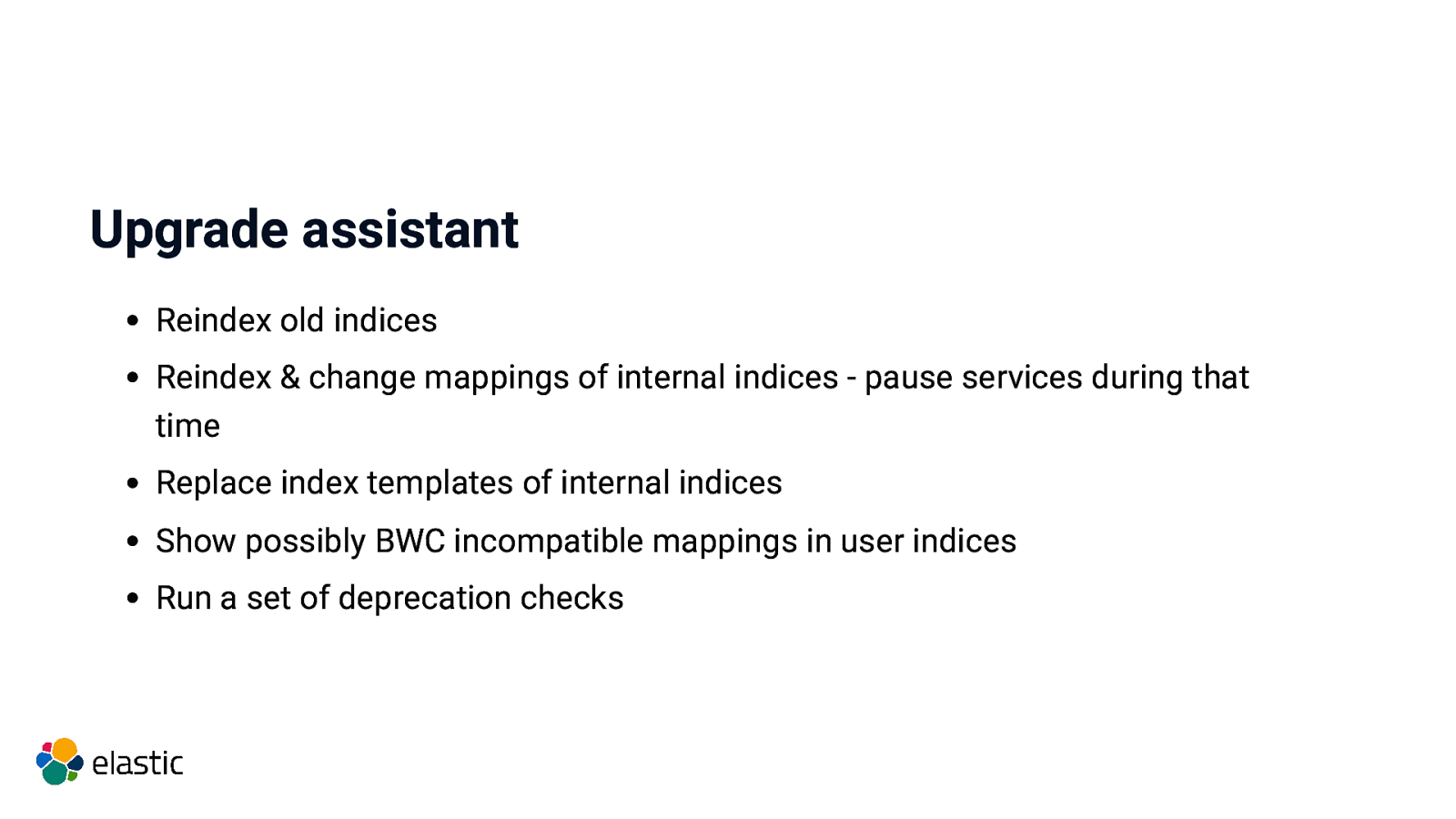
Upgrade assistant Reindex old indices Reindex & change mappings of internal indices - pause services during that time Replace index templates of internal indices Show possibly BWC incompatible mappings in user indices Run a set of deprecation checks
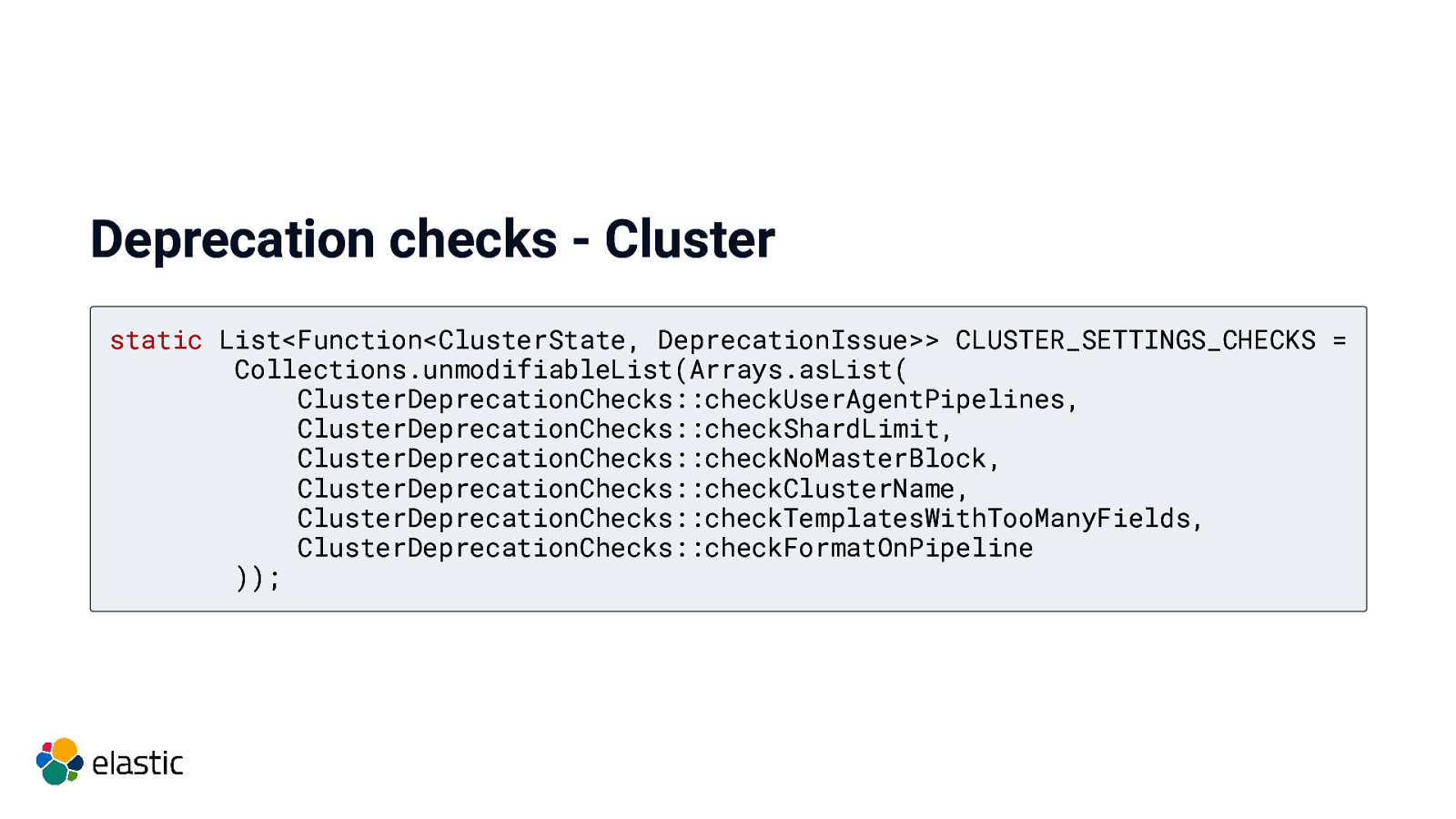
Deprecation checks - Cluster static List<Function<ClusterState, DeprecationIssue>> CLUSTER_SETTINGS_CHECKS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList( ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkUserAgentPipelines, ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkShardLimit, ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkNoMasterBlock, ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkClusterName, ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkTemplatesWithTooManyFields, ClusterDeprecationChecks::checkFormatOnPipeline ));
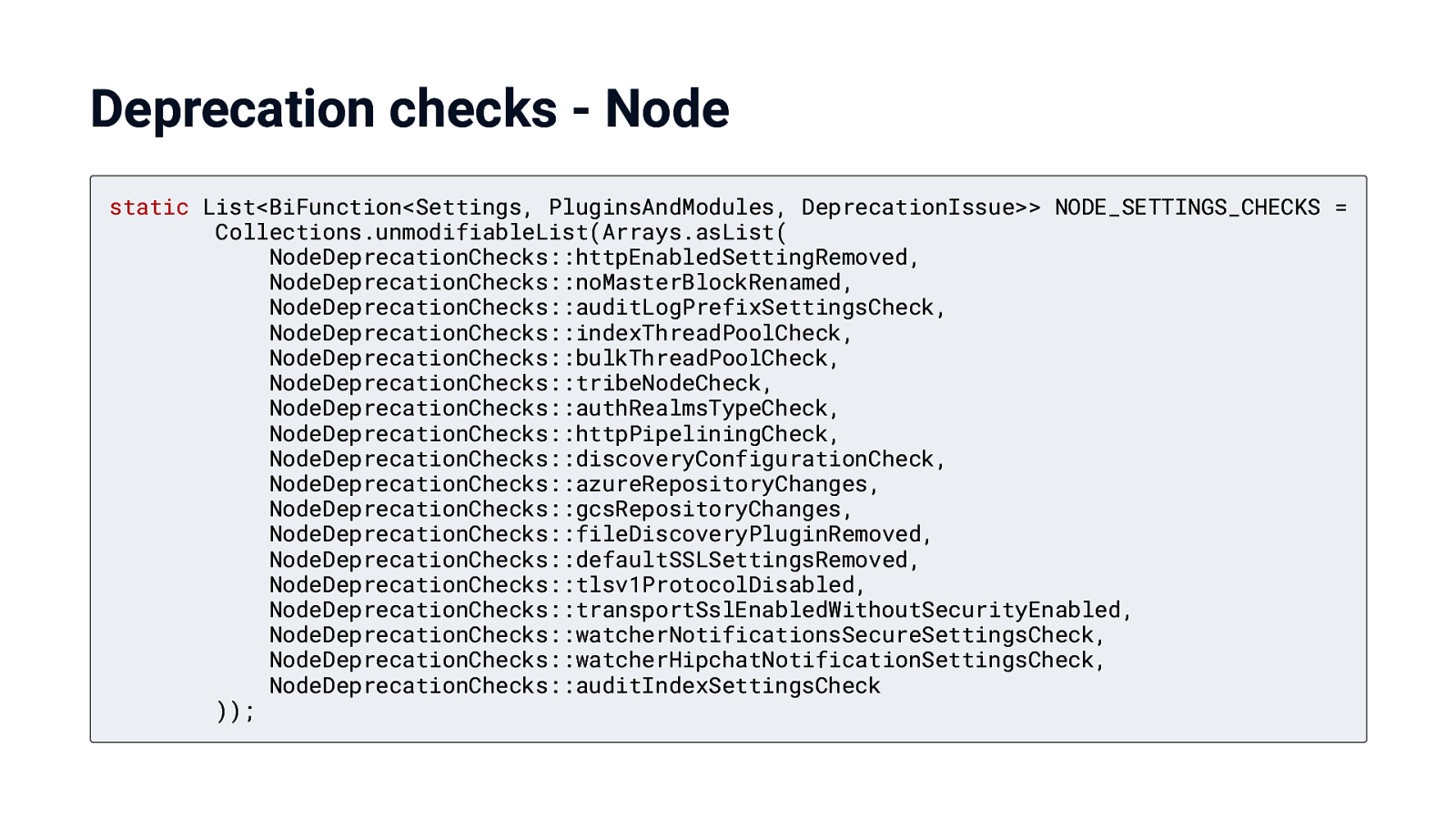
Deprecation checks - Node static List<BiFunction<Settings, PluginsAndModules, DeprecationIssue>> NODE_SETTINGS_CHECKS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList( NodeDeprecationChecks::httpEnabledSettingRemoved, NodeDeprecationChecks::noMasterBlockRenamed, NodeDeprecationChecks::auditLogPrefixSettingsCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::indexThreadPoolCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::bulkThreadPoolCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::tribeNodeCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::authRealmsTypeCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::httpPipeliningCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::discoveryConfigurationCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::azureRepositoryChanges, NodeDeprecationChecks::gcsRepositoryChanges, NodeDeprecationChecks::fileDiscoveryPluginRemoved, NodeDeprecationChecks::defaultSSLSettingsRemoved, NodeDeprecationChecks::tlsv1ProtocolDisabled, NodeDeprecationChecks::transportSslEnabledWithoutSecurityEnabled, NodeDeprecationChecks::watcherNotificationsSecureSettingsCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::watcherHipchatNotificationSettingsCheck, NodeDeprecationChecks::auditIndexSettingsCheck ));

Deprecation checks - Index static List<Function<IndexMetaData, DeprecationIssue>> INDEX_SETTINGS_CHECKS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList( IndexDeprecationChecks::oldIndicesCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::delimitedPayloadFilterCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::percolatorUnmappedFieldsAsStringCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::indexNameCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::nodeLeftDelayedTimeCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::shardOnStartupCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::classicSimilarityMappingCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::classicSimilaritySettingsCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::tooManyFieldsCheck, IndexDeprecationChecks::deprecatedDateTimeFormat ));

Deprecation checks - Machine Learning static List<BiFunction<DatafeedConfig, NamedXContentRegistry, DeprecationIssue>> ML_SETTINGS_CHECKS = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList( MlDeprecationChecks::checkDataFeedAggregations, MlDeprecationChecks::checkDataFeedQuery ));

Deprecation checks - only a partial solution Elasticsearch only Configuration only How to inform about deprecated queries?

Stack deprecations Write deprecation logs to a datastream #46106 Surface this information properly within Upgrade Assistant Allow others components to the stack to write to that index

Testing Automated rolling upgrade test Automated full cluster restart test Automated mixed cluster

Example: Switch from joda to java time Joda time only supports millisecond resolution + maintenance mode JDK has java.time API, supporting nanosecond resolution JDK and Joda time are different beasts

Joy of date formats @Test public void testSameFormat() { final ZonedDateTime endOfYear = ZonedDateTime.parse(“2019-12-31T00:00:00.000Z”); final long millis = endOfYear.toInstant().toEpochMilli(); final String jodaYear = DateTimeFormat.forPattern(“YYYY”).print(millis); final String javaYear = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(“YYYY”).format(endOfYear); assertThat(jodaYear).isEqualTo(javaYear); }
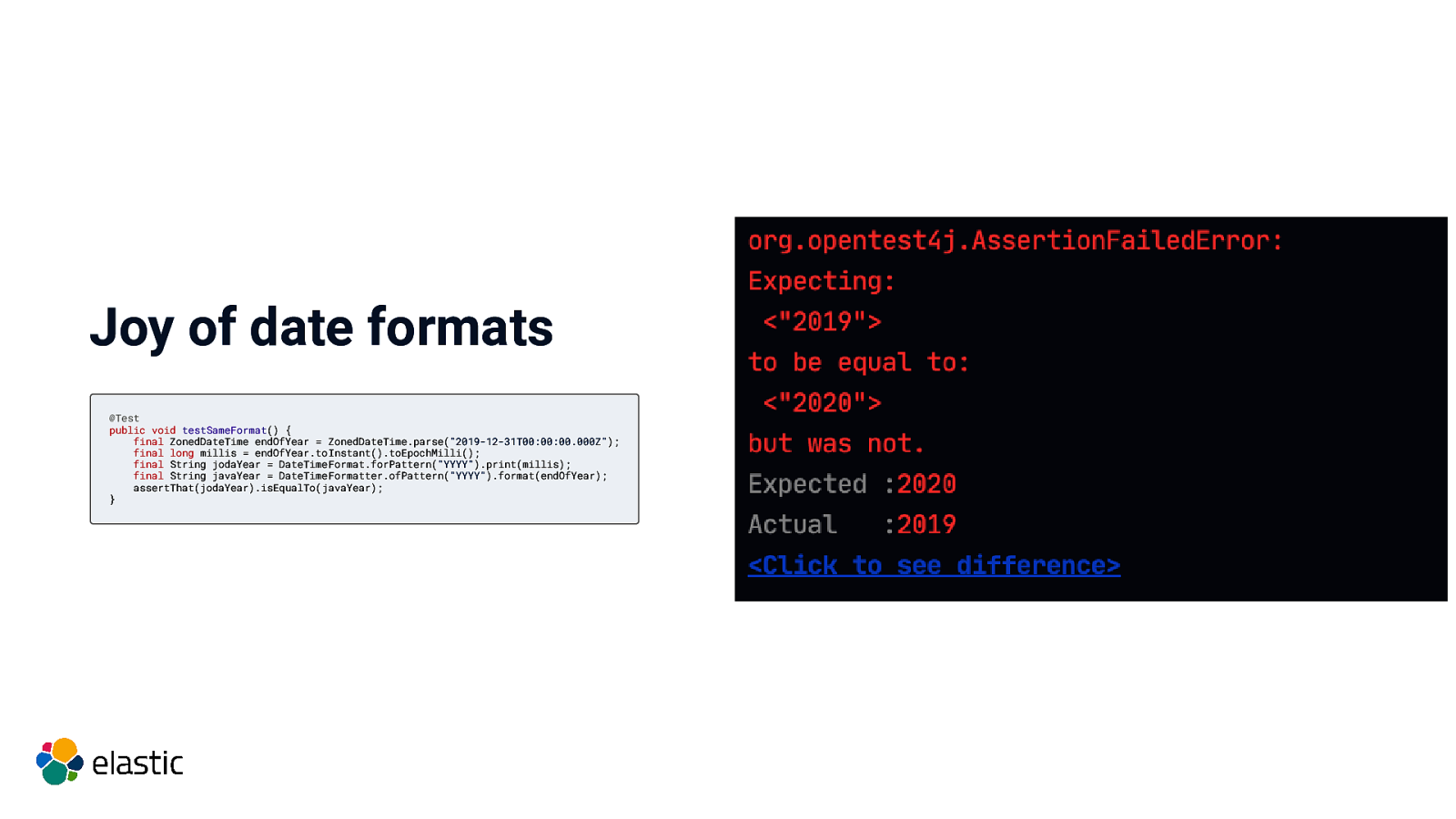
Joy of date formats @Test public void testSameFormat() { final ZonedDateTime endOfYear = ZonedDateTime.parse(“2019-12-31T00:00:00.000Z”); final long millis = endOfYear.toInstant().toEpochMilli(); final String jodaYear = DateTimeFormat.forPattern(“YYYY”).print(millis); final String javaYear = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(“YYYY”).format(endOfYear); assertThat(jodaYear).isEqualTo(javaYear); }

Example: Switch from joda to java time 6.x: Using yyyy-MM-dd uses joda time 6.8: Emit deprecation warning when certain joda date formats were used 6.8 & 7.x: Support 8uuuu-MM-dd as format with java time in mappings 7.x: Using uuuu-MM-dd uses java.time 7.x: Emit deprecation warning if date with 8 prefix is used 8.0: Drop support for 8 prefixed date formats 8.0: Remove joda dependency

Example: Remove types from indices 5.x: Arbitrary types are supported 6.x: Indices can only have a single type 6.x: Old 5.x indices can still be read with several types 6.x: New indices with several types cannot be created 6.x: Pseudo type _doc is used as a placeholder 7.x: Indices do not have any type 7.x: APIs with types in the URL are marked as deprecated 8.x: APIs with types in the URL are removed

Example: REST API version compatibility #51816 REST API is the external communication interface for all clients Major versions could break endpoints or request structure Upgrading all clients in the correct order might be impossible First candidate: Allow compatibility for types

Strategy: REST client throwing exceptions on deprecations Treat deprecations as failures (and enable in CI) RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost(…)) .setStrictDeprecationMode(true) .build();

Strategy: Reindex from remote Upgrading from 2.x to 7.x would require two reindexing steps I/O & CPU heavy Using reindex from remote the newer cluster could pull from the older one One time indexing cost, scripting is supported

Strategy: Replace clusters over time with CCS Assumption: Time series data grows out over time Instead of reindexing, use a second cluster to index current time series data When querying, use Cross Cluster Search to query both clusters CCS allows to query three different major versions (one up, one down, current) At some point, the old cluster can be shut down, once the data has aged out

Example: Removal of delete-by-query Delete by Query functionality could lead to different data between shard copies Inacceptable, functionality removed, immediately User reaction: Documented steps to achieve this in a safe way via existing APIs Next major: Added infrastructure for long running tasks in the background Implemented delete by query using long running tasks

Summary No BWC == maintenance forever Preparation: Deprecation warnings Migration: Allow parallel operations, rolling upgrades Document breaking changes! Marathon over several major versions Removing functionality: Be explicit, help! Adding functionality: You own it! No feature, no future BWC issues. Figure out user migration painpoints SaaS: Offer one click upgrades, so users only have to prepare their apps!

Can you quantify BWC cost

Thanks for listening Q&A Alexander Reelsen Community Advocate alex@elastic.co | @spinscale

Resources Upgrading the Elastic Stack Kibana Upgrade Assistant Deprecation logging

Community & Meetups https://community.elastic.co
Discuss Forum https://discuss.elastic.co

Thanks for listening Q&A Alexander Reelsen Community Advocate alex@elastic.co | @spinscale